2.4 Innovators and pioneers
“ education doesn’t need to be reformed -- it needs to be transformed. The key to this transformation is not to standardize education, but to personalize it— Sir Ken Robinson
The pioneers in education of the new millennium do not merely ask for the evolution of the existing system, but also for revolutionary changes from the base to the higher and upper levels. Many theories and suggestions have been heard. According to some of these, the curriculum should be individually adjusted, based on the talents and interests of every young person. The education should avoid subjugating and dominating young people, whereas it should foster curiosity and creativity1. Knowledge should be sought in more than one sources and areas so that the students will receive information beyond the boundaries of classroom, while the new technologies should be used to contribute positively to this pattern. The relationship between the teacher and the student has changed in the coming years, the classroom has become completely digitized and it has gradually lost its role as the center of education.
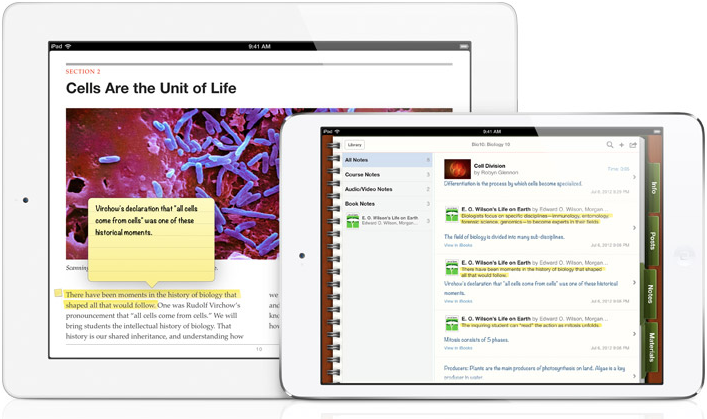
The most contemporary educational institutions and independent educational organizations have realized that the new technologies do not pose any danger to education, but on the contrary they are an ally. Modern systems serving the needs of entire universities, such as the blackboard2, have incorporated portable devices into their system and they use them as a key tool. Apple, the Information Technology Company, through iTunes U3, the new platform it has launched, is trying to establish its tablets as an essential tool for the contemporary education.
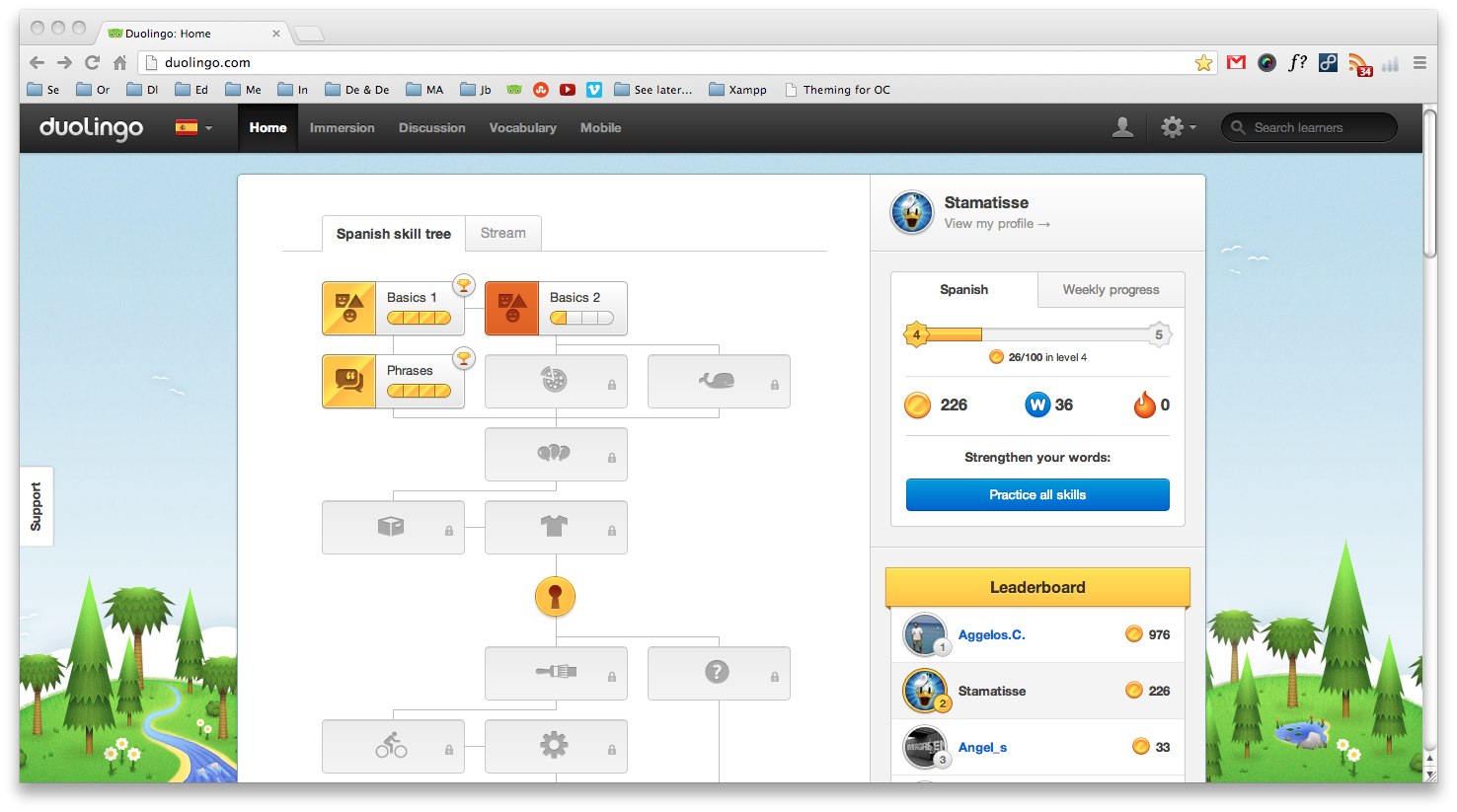
The prospects for interrelation, communication and collaboration have brought about new opportunities and ways to acquire knowledge. It is not a coincidence that in the recent years many institutions have emerged offering their courses online for free or upon payment. The tools are constantly updated and improved over the last years, offering solutions to many common problems. Duolingo4 is a platform that offers free high quality services on education. Coursera5 is one of the most important platforms, providing massive open online courses (MOOC), with courses from major universities worldwide. The sheer volume of students and the assignments to be corrected led to the introduction of new methods of online teaching and the creation of tools and correction methods that are incredibly helpful to the teachers. Skillshare6 removes the time pressure from the process of lesson and the delivery of assignments.